The induction of Triticum aestivum L. tolerance to Septoria tritici by oxalic acid
Abstract
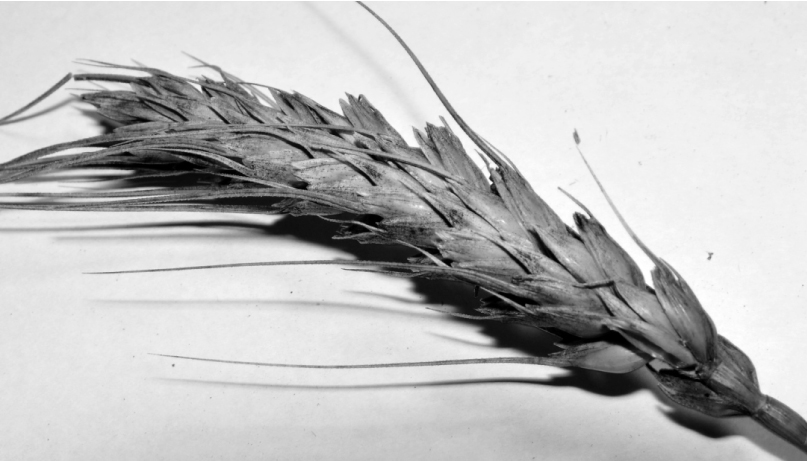
The influence of fungus Septoria tritici on winter wheat (Triticum aestivum) cultivars ‘Polis´ka 90’ and ‘Stolychna’ yield formation and plant development, as well as protective role of oxalic acid were studied in the field experiment. It was shown that treatment by oxalic acid decreases the infected square of flag leaves, ears and stems in both varieties that normalized plant development and reduced the yield loss. The usage of elicitors is the way to induce the plant immunity of cereals and minimize the pesticide pollution of the environment.
References
Дмитриев А.П., Гродзинский Д.М., Полищук В.П. 2005. Индуцирование системной устойчивости у растений биогенными индукторами. Вісник Харківського націон. аграрного університету. Серія Біологія 3: 24–36.
Жук І.В., Лісова Г.М., Довгаль З.М., Дмитрієв О.П. 2013. Вплив оксиду азоту та щавлевої кислоти на ураження рослин пшениці (Triticum aestivum L.) септоріозом. Mod. Phytomorphol. 4: 387–391.
Жук І.В., Дмитрієв О.П. 2013. Індукція захисних реакцій пшениці, інфікованої збудником септоріозу. Фактори експериментальної еволюції організмів 12: 219–223.
Захаренко В.А., Овсянкина А.В., Санин С.С. и др. 2003. Карты распространения вредных организмов, патотипов, генов вирулентности возбудителей болезней, фитофагов, энтомопатогенов на территории Российской Федерации. Россельхозакадемия, Москва.
Шакирова Ф.М. 2001. Неспецифическая устойчивость растений к стрессовым факторам и ее регуляция. Гилем, Уфа.
Cessna S.G., Sears V.E., Dickman M.B., Low P.S. 2000. Oxalic acid, a pathogenicity factor for Sclerotinia sclerotiorum suppresses the oxidative burst of the host plant. Plant Cell 12: 2191–2199.
Dumas B., Freyssinet C., Pallett K.E. 1995. Tissue-specific expression of cermin-like oxalate oxidase during development and fungal infection of barley seedlings. Plant Physiol. 107: 1091–1096.
Franceschi V.R., Nakata. P.A. 2005. Calcium oxalate in plants: formation and function. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 56: 41–71.
Kayashima T., Katayama T. 2002. Oxalic acid is available as a natural antioxidant in some systems. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1573: 1–3.
Lane B.G. 2002. Oxalate, germins, and higher-plant pathogens. Life 53: 67–75.
Toal E.S., Jones P.W. 1999. Induction of systemic resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum by oxalic acid in oilseed rape. Plant Pathol. 48: 759–767.


This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The journal is licensed by Creative Commons under BY-NC-ND license. You are welcome and free to share (copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format) all the published materials. You may not use the material for commercial purposes. You must give appropriate credit to all published materials.
The journal allow the author(s) to hold the copyrights and to retain publishing rights without any restrictions. This is also indicated at the bottom of each article.