Impact of light spectral composition on the length and weight of the gametophyte of Polytrichastrum formosum (Hedw.) G.L. Smith, Plagiomnium cuspidatum (Hedw.) T.J. Kop. and Pleurozium schreberi (Brid.) Mitt.
Abstract
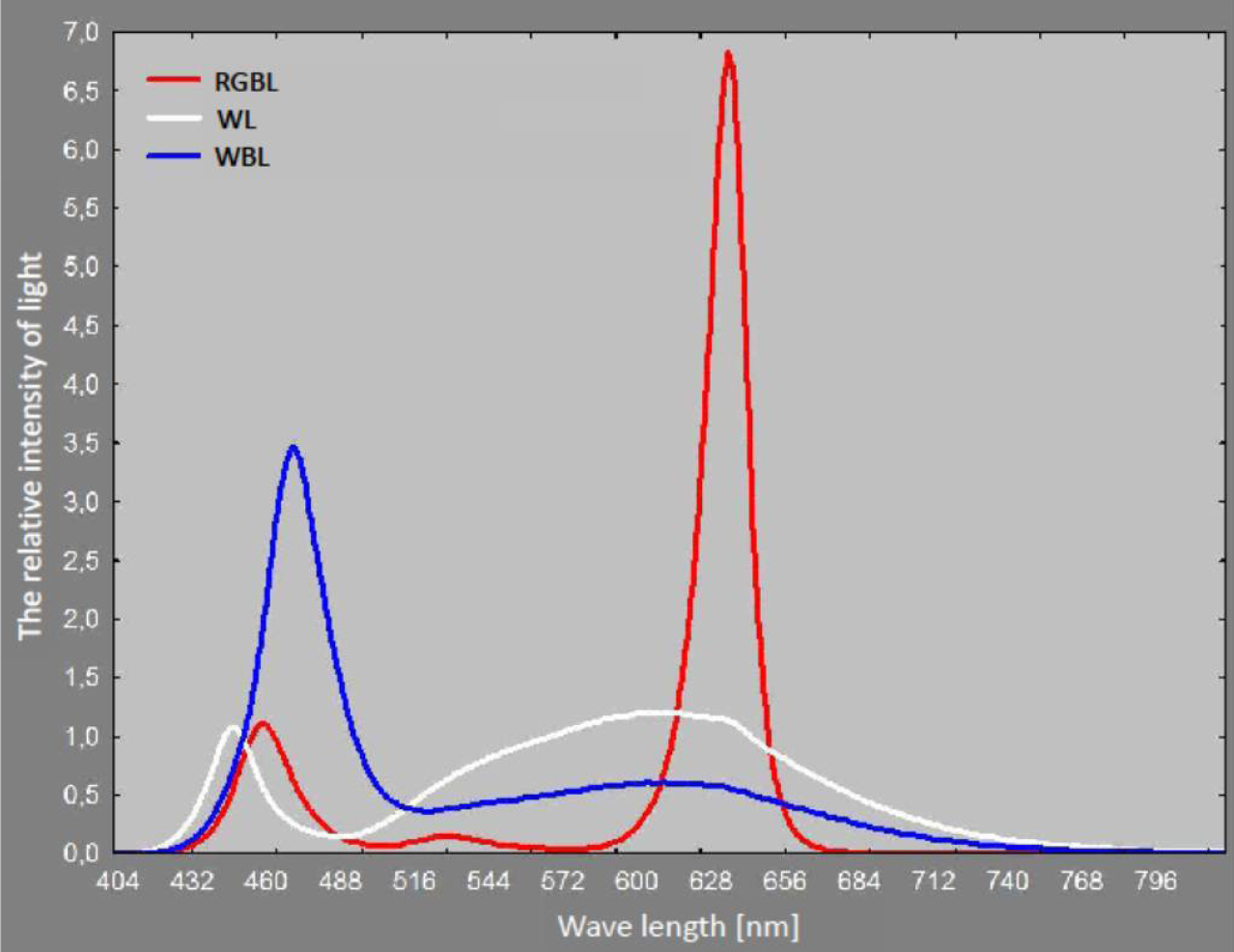
The aim of the present study was to examine the influence of light spectral composition on the length and weight of mosses gametophytes: Polytrichastrum formosum (Hedw.) G.L. Smith, Plagiomnium cuspidatum (Hedw.) T.J. Kop. and Pleurozium schreberi (Brid.) Mitt. Plants were grown 31 days in the chambers equipped with LEDs matrices of the same intensity of light (200 µmol m-2 · s-1), but different spectral composition: white (WL), white-blue (WBL) and red-green-blue (RGBL). It was found that the WBL as compared to RGBL inhibited the growth of the whole gametophytes of P. cuspidatum and P. formosum. WBL inhibited also rhizoids length of P. cupsidatum, in comparison to plants growing on WL and RGBL as well as growth of leaves stalks P. schreberi and P. cuspidatum as compared to WL. For RGBL fresh weight of plants P. cuspidatum was significantly higher than the WBL, while in P. schreberi higher than that for WBL and WL. Impact of light quality on the dry matter production was observed only in P. schreberi. Effect of spectral composition of light on the length and weight of the gametophyte depends on the species of moss.
References
Cerff M., Posten C. 2012. Relationship between light intensity and morphology of the moss Physcomitrella patens in a draft tube photo bioreactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 60: 119–126.
Franklin K.A., Larner V.S., Whitelam G.C. 2005. The signal transducing photoreceptors of plants. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 49 (5-6): 653–664.
Gumiński S. 1990. O wpływie światła niebieskiego i nadfioletowego na zjawiska morfogeniczne i niektóre metaboliczne u roślin. Wiad. Bot. 34 (3): 5–13. (in Polish)
Hetmann A., Kowalczyk S. 2011. Potranslacyjne modyfikacje czynników transkrypcyjnych PIF/PIL jako efekt rozkodowywania przez fitochromy sygnałów świetlnych. Postępy Biol. Komórki 38 (1): 19–42. (in Polish)
Huttunen S., Lappalainen N.M., Turunen J. 2005. UV-absorbing compounds in subartictic herbarium bryophytes. Environ. Pollut. 133: 303–314.
Kern V.D., Sack F.D. 1999. Red light-induced suppression of gravitropism in moss protonemata. Adv. Space Res. 24 (6): 713–716.
Lamparter T., Hughes J., Hartmann E. 1998. Blue light- and genetically-reserved gravitropic response in protonemata of the moss Ceratodon purpureus. Planta 206: 95–102.
Li H., Tang C., Xu Z., Liu X., Han X. 2012. Effects of different light sources on the growth of non-heading Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L.). J. Agricult. Scie. 4 (4): 262–273.
Matioc-Precup M.M., Cachiţă-Cosma D. 2012. The germination and growth of Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata f. rubra plantlets under the influence of colored light of different provenance. Stud. Univer. “Vasile Goldiş”’ Seria Ştiinţele Vieţii 22 (2): 193–202.
Pasentsis K., Paulo N., Algarra P., Dittrich P., Thümmler F. 1998. Characterization and expression of the phytochrome gene family in the moss Ceratodon purpureus. Plant J. 13 (1): 51–61.
Pilarski J. 2005. Na świetle i w mroku. Academia 4 (4): 33–35.
Rzepka A. 2008. Ekofizjologiczne aspekty reakcji różnych gatunków mchów na abiotyczne czynniki stresowe. Praca monograficzna: 9–12. Wydawnictwo Naukowe AP, Kraków. (in Polish)
Skoczowski A., Czyczyło-Mysza I., Skwarek A., Pilarski J., Grzesiak W., Nowak T. 2010. Impact of light spectra composition and ozone fumigation on chlorophyll content changes and optical properties of broccoli leaves. Zesz. Probl. Postępów Nauk Rol. 545: 357–373.
Suetsugu N., Wada M. 2003. Cryptogam blue-light photoreceptors. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 6: 91–96.
Szafran B. 1963. Flora słodkowodna Polski, Musci – Mchy. T. 16. PWN, Warszawa. (in Polish)
Szweykowska A., Szweykowski J. 2002. Botanika (Systematyka): 198–213. PWN, Warszawa. (in Polish)
Wang H., Gu M., Cui J., Shi K., Zhou Y., Yu J. 2009. Effects of light quality on CO2 assimilation, chlorophyll-fluorescence quenching, expression of Calvin cycle genes and carbohydrate accumulation in Cucumis sativus. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. 96: 30–37.
Zeidler M., Lamparter T., Hughes J., Hartmann E., Remberg A., Braslavsky S., Schaffner K., Gärtner W. 1998. Recombinant phytochrome of the moss Ceratodon purpureus: heterologous expression and kinetic analysis of Pr-->Pfr conversion. Photochem. Photobiol. 68 (6): 857–863.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The journal is licensed by Creative Commons under BY-NC-ND license. You are welcome and free to share (copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format) all the published materials. You may not use the material for commercial purposes. You must give appropriate credit to all published materials.
The journal allow the author(s) to hold the copyrights and to retain publishing rights without any restrictions. This is also indicated at the bottom of each article.