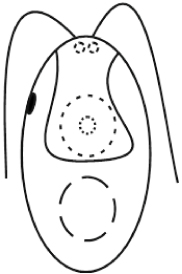
Cell types and their status in Chlamydomonas-like algae (Chlorophyceae) on agar medium culture
Abstract
The classification of cell types under agar culture was proposed. Six cell morphotypes were allocated. The statuses were identified depending on the reduction of monade attributes of cells. The variants of transition from one cell morphotype to another under dissolving mucilage were shown.
The monade, cocciod, palmeloid and gloeocysta morphotypes approximately equally represented in all clades. The asterococcus and mucogleocysta morphotypes presented only in Reinhardtinia аnd Oogamochlamydinia clades. Any morphotype isn’t typical for all clades of Chlamydomonas-like algae at once.
The most of morphotypes numbers (5 from 6) are presented in Reinhardtinia clade. This demonstrates the diversity of the Reinhardtinia clade species. There are only one morphotype presented in Polytominia and Monadinia clades. There are four morphotypes presented in Oogamochlamydinia clade, three – in Moewusinia, two morphotypes – in Chloromonadinia.
References
Костиков И.Ю., Демченко Э.Н., Новохацкая М.А. 2009. Коллекция культур водорослей Киевского национального университета имени Тараса Шевченко. Каталог штаммов (2008 г.). Черноморский ботан. журн. 5 (1): 37–79.
Павловська М.М., Костіков І.Ю. 2010. Швидкість переходу в монадний стан, як допоміжний критерій при ідентифікації видів роду Chlamydomonas (Chlorophyta). Чорноморський ботан. журн. 6 (4): 508–512.
Catt J., Hills G., Roberts K.A. 1976. Structural glycoprotein, containing hydroxyproline, isolated from the cell wall of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Planta 131 (2): 165–171.
Demchenko E., Mikhailyuk T., Coleman A.W., Pröschold T. 2012. Generic and species concepts in Microglena (previously the Chlamydomonas monadina group) revised using an integrative approach. Eur. J. Phycol. 47 (3): 264–290.
Ettl H. 1983. Chlorophyta. 1. Phytomonadina. In: Ettl H., Gerloff J., Heynig H., Mollenhauer D. (eds). Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bd. 9: 1-807. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart – New York.
List of Media and Recipes 2013. Experimental Phycology and culture collection of algae at the University of Goettingen (EPSAG). Goettingen. http://www.uni-goettingen.de/en/186449.html
Nakada T., Misawa K., Nozaki H. 2008. Molecular systematics of Volvocales (Chlorophyceae, Chlorophyta) based on exhaustive 18S rRNA phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 48: 281–291.
Pröschold T., Marin B., Schlösser U.G., Melkonian M. 2001. Molecular phylogeny and taxonomic revision of Chlamydomonas (Chlorophyta). I. Emendation of Chlamydomonas Ehrenberg and Chloromonas Gobi, and description of Oogamochlamys gen. nov. and Lobochlamys gen. nov. Protist. 152: 265–300.
Roberts K. 1974. Crystalline glycoprotein cell walls of algae: their structure, composition and assembly. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 268 (891): 129–146.
Woessner J., Goodenough U. 1994. Volvocine cell walls and their constituent glycoproteins: An evolutionary perspective. Protoplasma 181 (1-4): 245–258.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The journal is licensed by Creative Commons under BY-NC-ND license. You are welcome and free to share (copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format) all the published materials. You may not use the material for commercial purposes. You must give appropriate credit to all published materials.
The journal allow the author(s) to hold the copyrights and to retain publishing rights without any restrictions. This is also indicated at the bottom of each article.